Sources of iron in a vegetarian diet
Contents:
- Iron in the human body
- Food sources of iron
- Iron sources in a meat-free diet
- What factors reduce the absorption of iron from plant products?
- Factors that improve the absorption of non-heme iron
Meat-free, vegetarian, and vegan diets, and their various variations, are becoming increasingly popular every year, and more and more people are choosing to abstain from consuming animal products. The reasons for such a decision can vary widely: from ethical, moral, and environmental to health-related. However, any of these elimination diets, if incorrectly formulated, can contribute to the development of nutrient deficiencies in the body. With meat-free diets, there is often a concern about a deficiency in easily absorbed iron, the largest and most reliable source of which is meat. So, how and what should you eat to maintain good health and not give up on a vegetarian or vegan diet?
Iron in the human body
Iron plays a role in the development of our immunity and functions as a component of enzymes involved in the synthesis of collagen and some neurotransmitters. About 70% of iron is found in hemoglobin, which delivers oxygen to the tissues, and in myoglobin (in muscle cells), which stores and releases it. About 6% of iron is part of the proteins necessary for respiration and energy metabolism. The rest of this ingredient is stored "in storage." Iron plays a role in the development of our immunity and functions as a component of enzymes involved in the synthesis of collagen and some neurotransmitters. Chronic iron deficiency can lead to the development of anemia, which negatively affects the body's performance and immunity. A deficiency of this element therefore leads to chronic fatigue, general weakness, difficulty concentrating, pale skin, shallow breathing, increased heart rate, and dizziness. In children, symptoms such as loss of appetite, delayed neurocognitive development, and an increased risk of infections may also occur. Pregnant women are at increased risk of premature birth.
Food sources of iron
There are two forms of iron in food: heme iron, which is found in animal products and is better absorbed by the body, and non-heme iron, which is found primarily in plant foods. Its availability from food is lower because it is susceptible to the influence of various absorption inhibitors. For this reason, it is recommended that people on a meat-free diet consume about 80% more iron than those on a mixed diet.
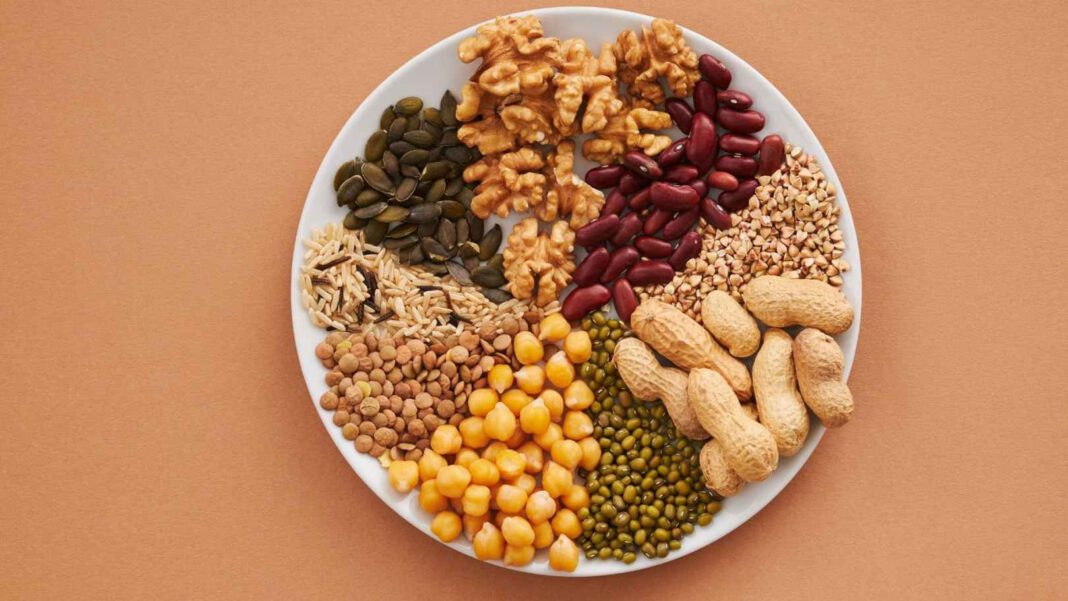
Iron sources in a meat-free diet
A properly composed vegan and vegetarian diet can provide the right amount of iron. The most important sources of iron in a meat-free diet are legumes, whole grains, seeds, and dried fruits. Egg yolks are a good source of iron in a vegetarian diet. Meat-free, iron-rich foods include:
- cooked: soybeans , lentils, white and red beans,
- Pumpkin seeds, sunflower seeds,
- Chia seeds ,
- Tofu,
- Tahini sesame paste ,
- Pistachios,
- Beetroot,
- Spinach,
- Mushrooms (chanterelles),
- Peanut butter ,
- Oatmeal,
- dried apricots , figs,
- Chicken eggs.
What factors reduce the absorption of iron from plant products?
Non-heme iron is less readily absorbed than iron from animal products. The absorption of non-heme iron depends on the composition of the food and even the specific meal. Therefore, in addition to the iron supply in the diet, the composition of meals is also of great importance in a meat-free diet. Substances that reduce iron absorption include:
- Polyphenols – they are found in black tea, among other things,
- Phytic acid – found in legumes, grains, nuts and seeds.
Factors that improve the absorption of non-heme iron
The process of iron absorption can be effectively supported by proper meal composition and by avoiding beverages rich in polyphenols. Adding vitamins A, C, beta-carotene, and organic acids to a meal is an effective way to increase non-heme iron absorption.
- Vitamins A, C, and beta-carotene neutralize the effects of phytic acid. Therefore, adding products rich in these ingredients to meals can help increase non-heme iron absorption by two to twelve times.
To ensure adequate iron intake on a meat-free diet, meals should be prepared from plant-based foods rich in this element, and each meal should be supplemented with a good source of vitamin C, such as fresh fruit, vegetables, or cucumbers . Products such as legumes, nuts, and oatmeal should be soaked before consumption. Tea and coffee, on the other hand, are best consumed at least an hour before or after meals. Choose juice or simply water to drink during meals.
THE PUBLISHER'S CHOICE
Dried plums 1 kg BIOGO
- €7,01
- €7,01
- Unit price
- / per
Dried White Mulberries 500 g ORGANIC
- €5,84
- €5,84
- Unit price
- / per
Almonds 1 kg BIOGO
- €11,69
- €11,69
- Unit price
- / per
Cranberries sweetened with apple juice organic 1 kg BIOGO
- €16,37
- €16,37
- Unit price
- / per
Dried dates 1 kg BIOGO
- €4,21
- €4,21
- Unit price
- / per
Unpeeled buckwheat groats 1 kg BIOGO
- €2,81
- €2,81
- Unit price
- / per
Walnuts 800 g BIOGO
- €8,65
- €8,65
- Unit price
- / per
Peeled sunflower seeds 1 kg BIOGO
- €3,04
- €3,04
- Unit price
- / per
PULLED ORGANIC SUNFLOWER SEEDS 1 KG BIOGO
- €4,44
- €4,44
- Unit price
- / per